Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Advancing innovation through cutting-edge materials research, education, and industry collaboration
Explore Postgraduate ProgramsAbout the Department
The Department of Materials Science and Engineering provides undergraduate and postgraduate education, research, advanced facilities for materials characterization, and active collaborations with industry and global partners.
Research Excellence
Pioneering innovations in Materials Science and Engineering
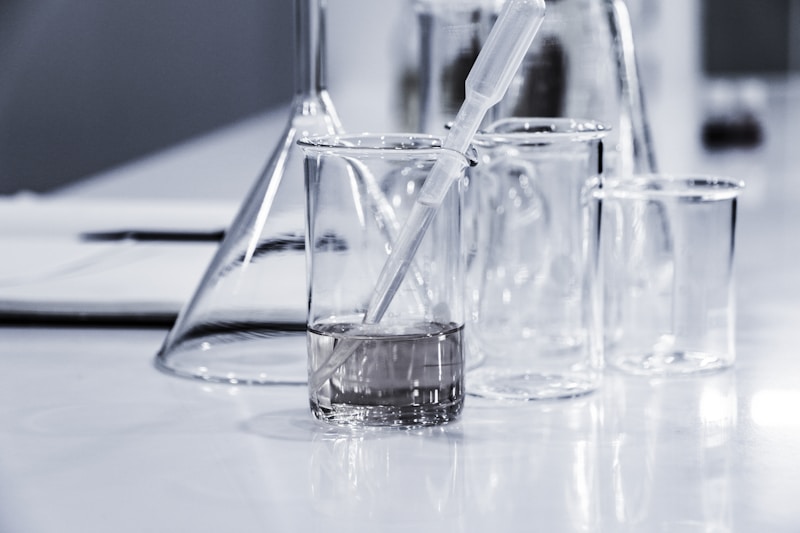
Our department conducts world-class research in advanced materials, nanotechnology, biomaterials, and sustainable energy solutions. With state-of-the-art facilities and expert faculty, we push the boundaries of what's possible in Materials Science and Engineering.
Our research impacts industries ranging from aerospace to healthcare, contributing to technological advancement and societal development.

Industry Partnerships
Bridging academia and industry for real-world impact
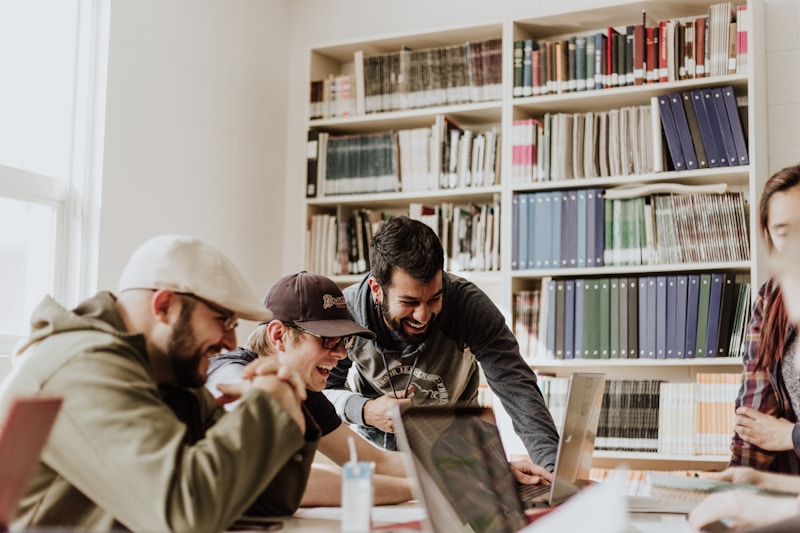
We collaborate with leading companies and organizations to solve complex materials challenges. Our partnerships provide students with practical experience and ensure our research addresses real-world needs.
From materials testing to consultancy services, we support industries in developing innovative solutions.

Exceptional Student Experience
Nurturing the next generation of Materials Science and Engineers
Our students benefit from hands-on learning experiences, cutting-edge laboratory facilities, and mentorship from world-renowned faculty. We offer comprehensive undergraduate and postgraduate programs designed to equip students with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
Join a vibrant community of learners and innovators shaping the future of Materials Science and Engineer.
Our Vision & Mission
Vision
Becoming a center of excellence in higher learning, research, industrial consultancy and other relevant activities in Materials Science and Engineering.
Mission
To be a center of excellence in Materials Science & Engineering by providing opportunity:
- for undergraduates and postgraduates to acquire specialized knowledge on the development and processing of engineering materials
- to conduct high-quality research to cater for national development
- to provide consultancy services to the public and private sector
Explore Our Department
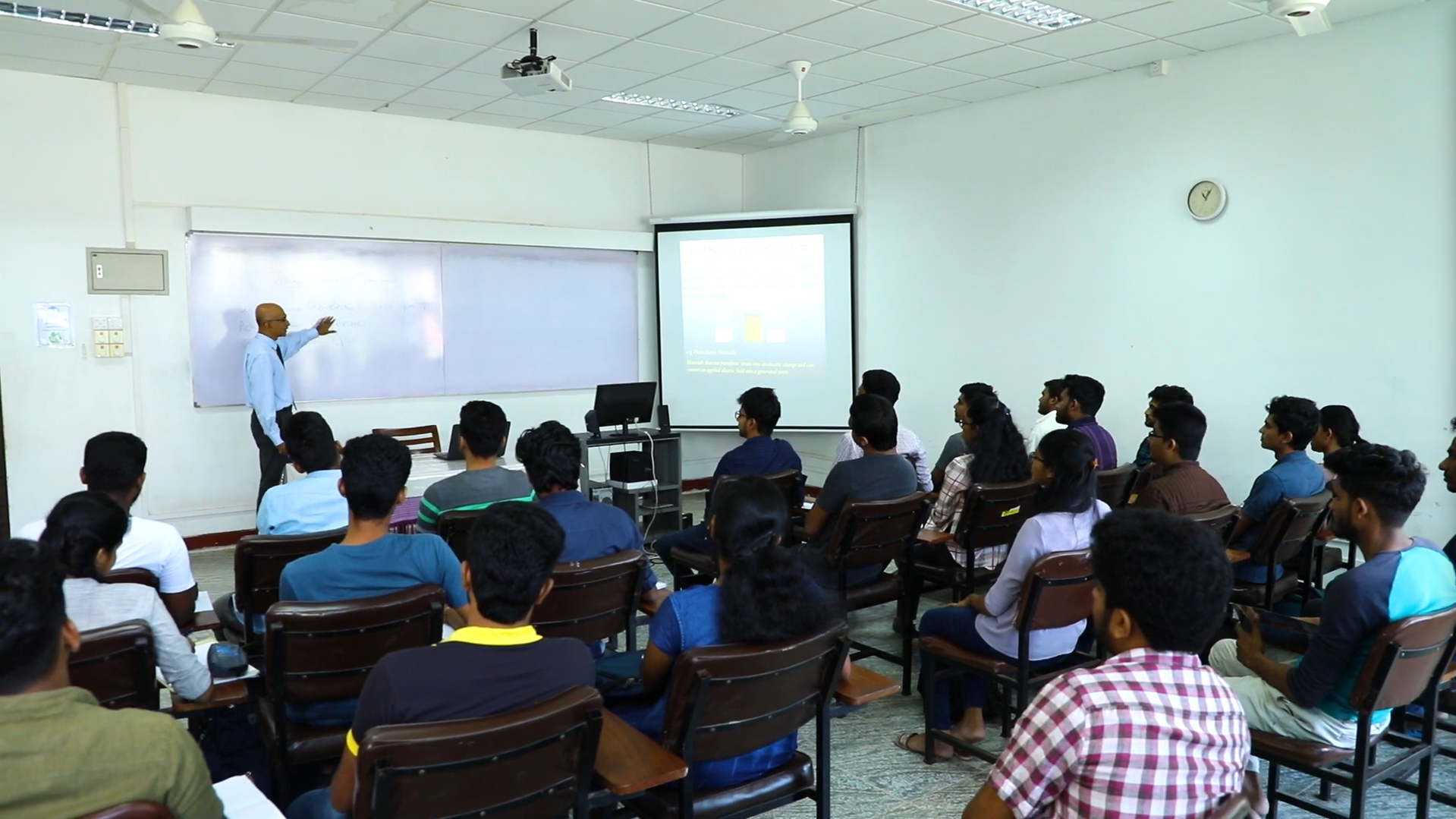

Undergraduate Programs
Bachelor of the Science of Engineering Honours in Materials Science and Engineering.
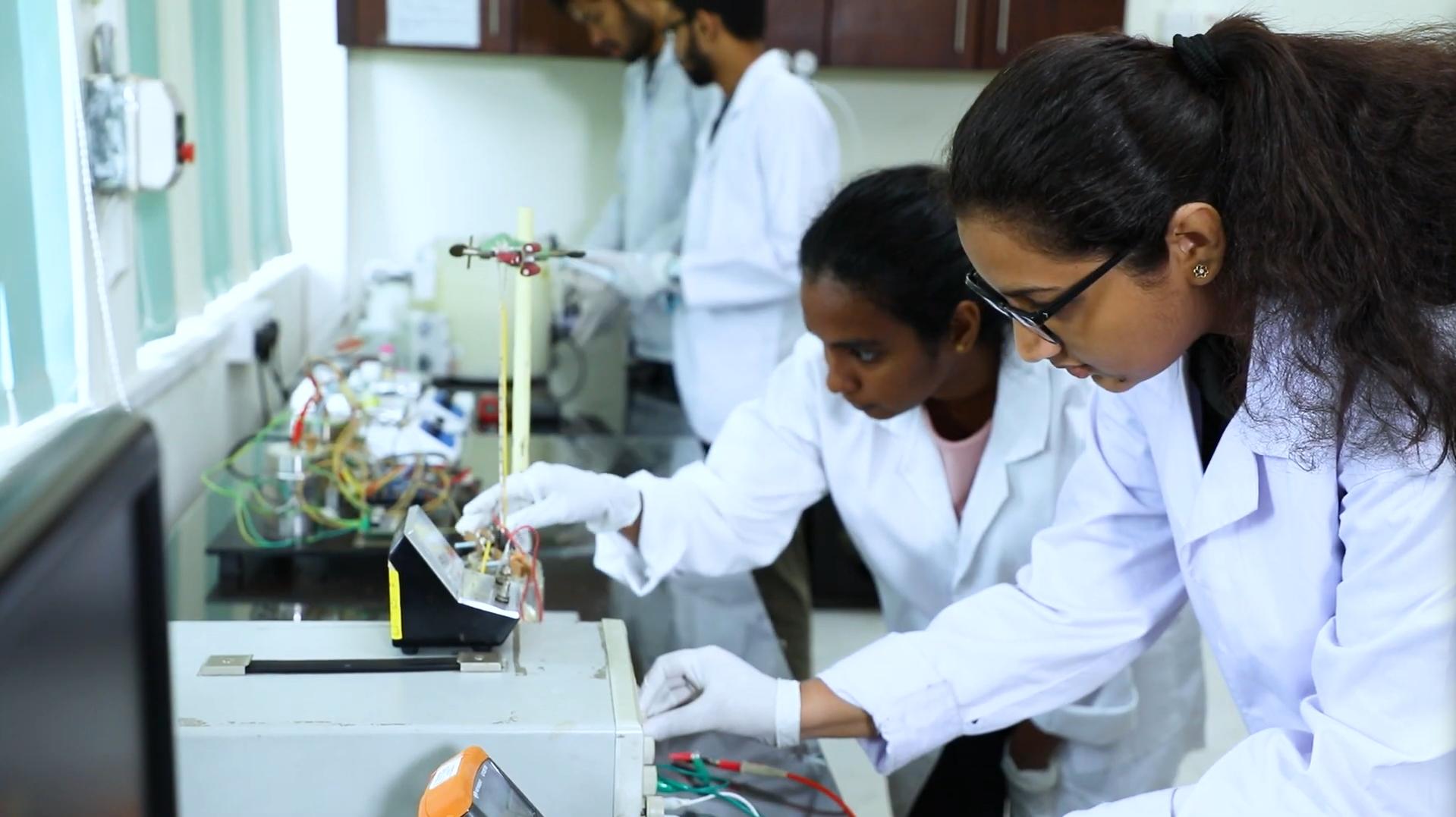

Postgraduate Programs
PhD, MPhil, MSc by research and coursework.
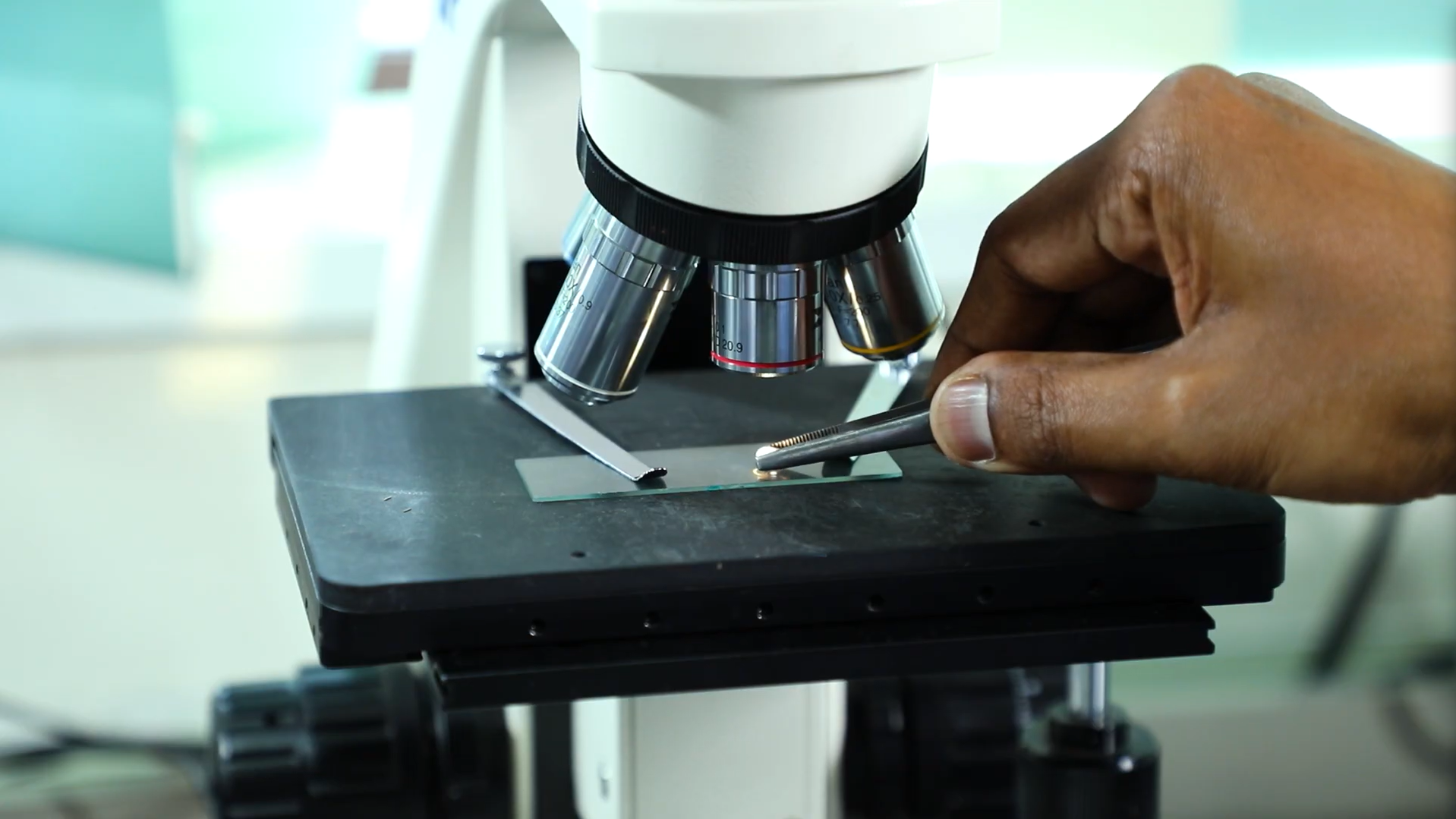

Research & Innovations
Fields covering Metallurgy, Ceramics, Polymers, Composites, Biomaterials, Nanomaterials, Energy materials, and more.
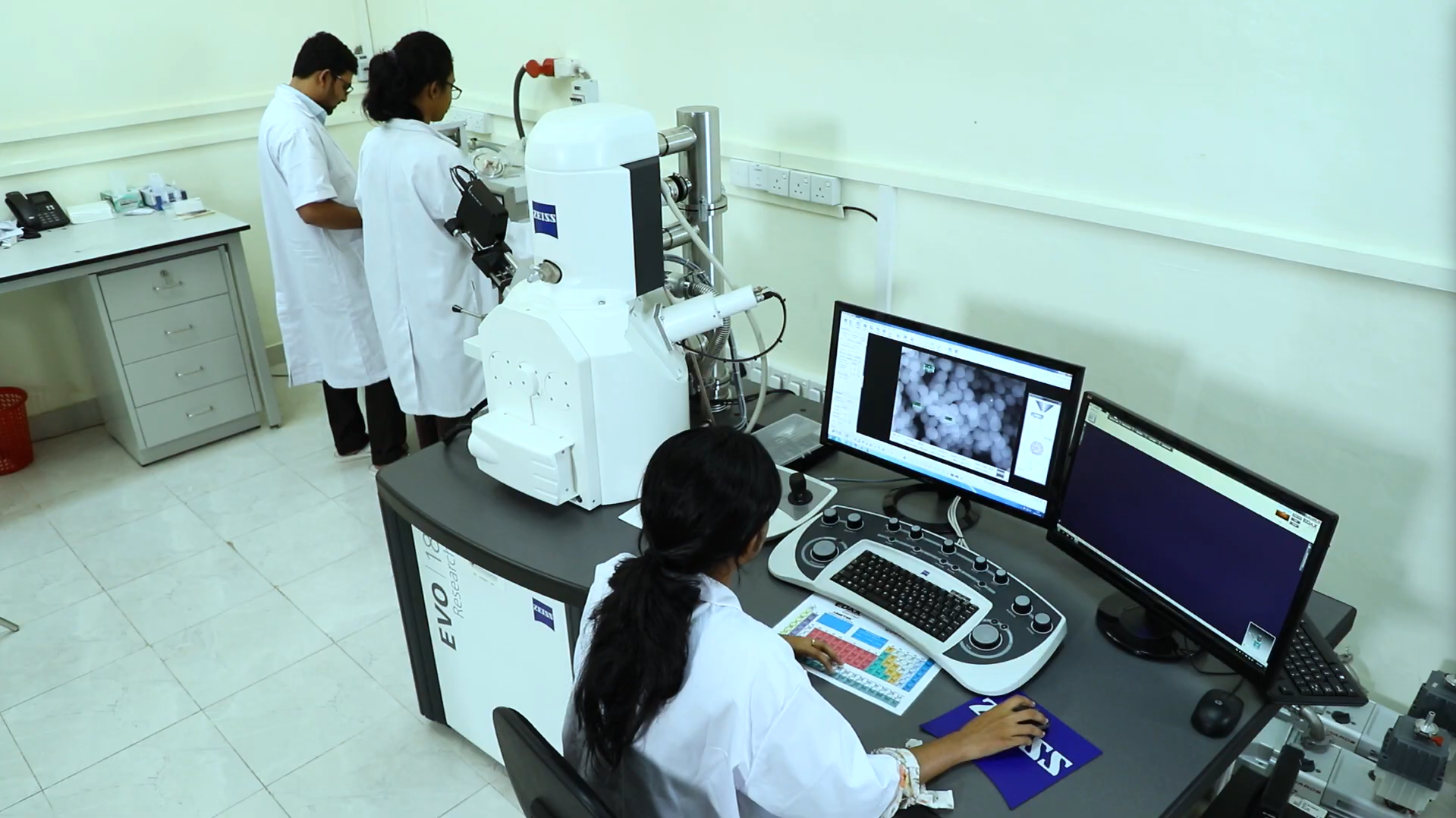

Facilities & Equipment
World-class laboratories and testing facilities supporting education, research and industry.

Academic Staff
Highly qualified academic staff with wide range of expertise.

Consultancy & Services
Expert advice, consultation services, and materials testing.
News & Events

Ada Derana Mornings - TV Segment
Highlighted the department's degree program, the upcoming Golden Jubilee Celebration, and the National Forum.

National Forum - MSE
A national gathering of experts, researchers, and industry leaders exploring how materials science.
